The Aerobic System. The aerobic system accesses a massive store of virtually unlimited energy. On this page you'll learn how this system will keep you chugging along forever without ever letting you get out of 2nd gear! The aerobic energy system utilises fats, carbohydrate and sometimes proteins for re-synthesising ATP for energy use.. It can include activities like brisk walking, swimming, running, or cycling. By definition, aerobic exercise means "with oxygen.". Your breathing and heart rate will increase during aerobic.

Aerobic system

PPT Aerobic Energy Systems PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1590875
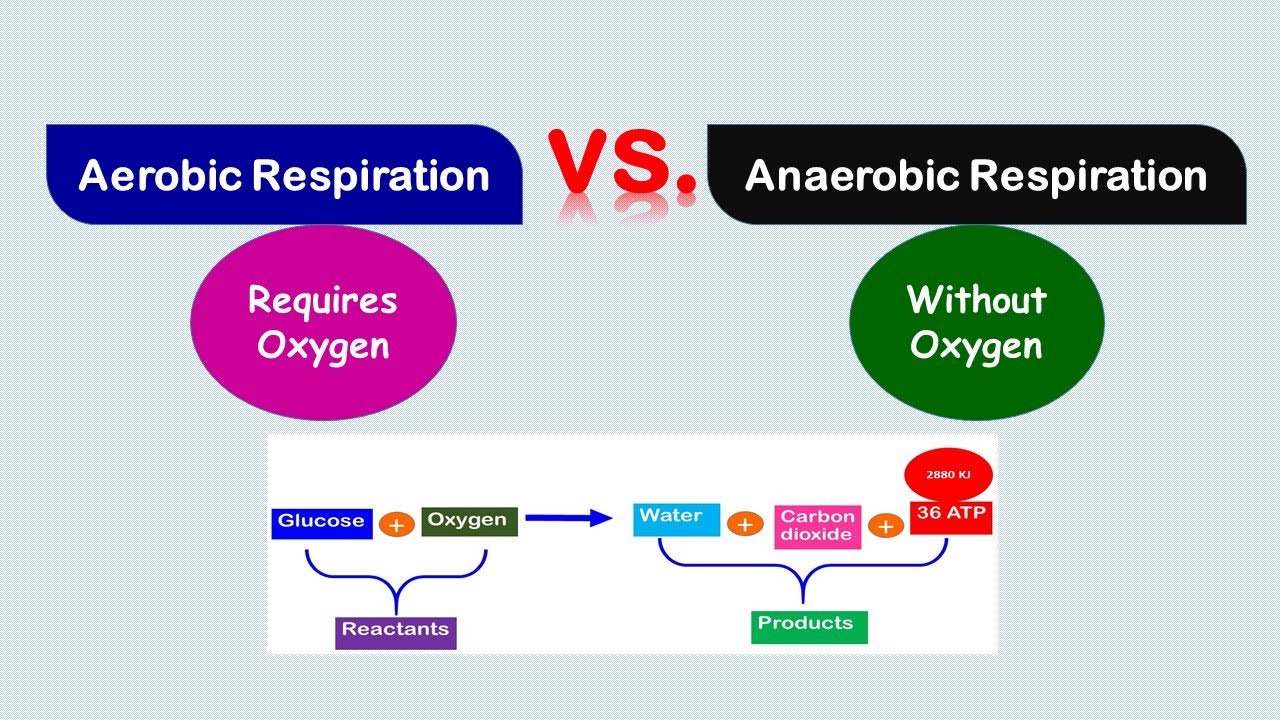
Gcse Pe A C Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration Energy Systems Vrogue

PPT THE EFFECT OF EXERCISE ON THE BODY SYSTEMS PowerPoint Presentation ID9120161
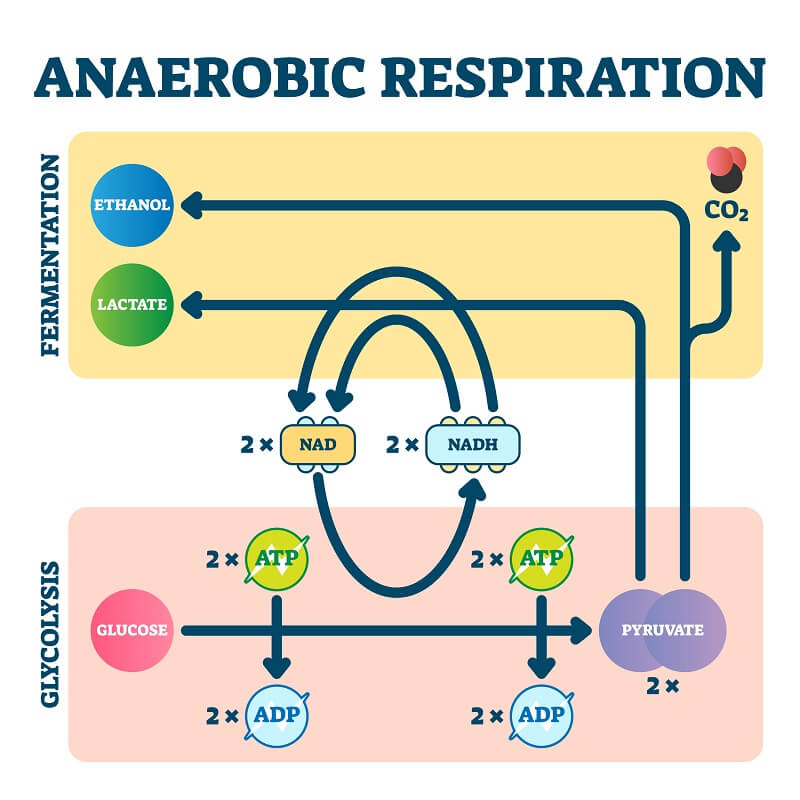
What is Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration? Definition, Difference

Aerobic system

What is Aerobic Exercise? CoreLife Healthcare

PPT Energy Systems for Exercise PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID671311
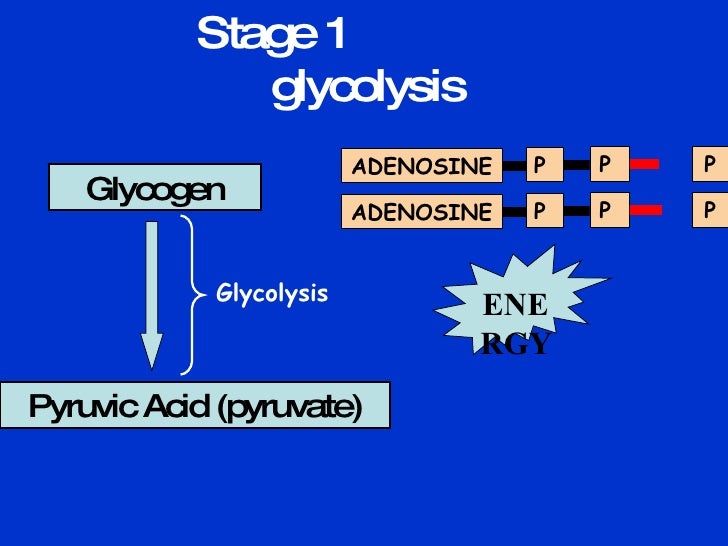
Aerobic system
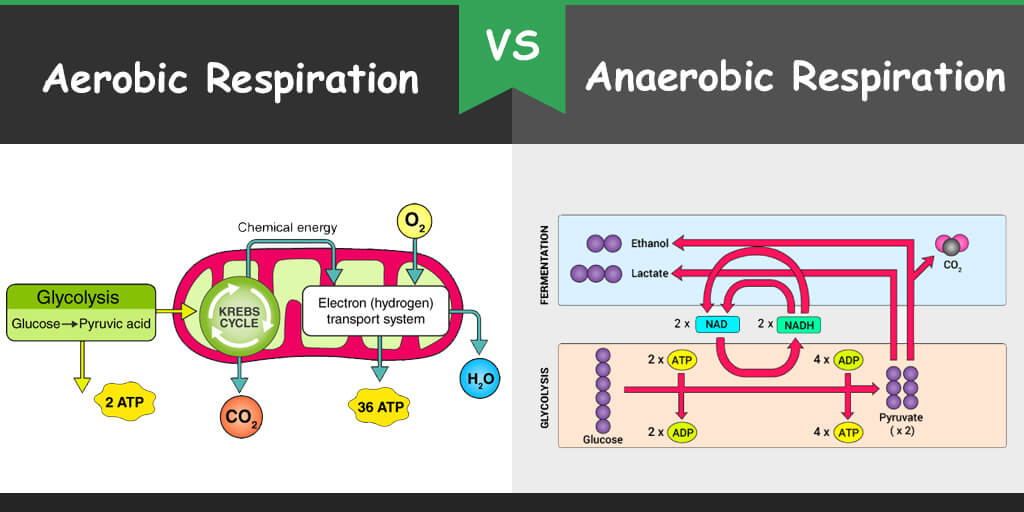
Difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Bio Differences

Aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration What are they? Differences

A2 PE AEROBIC ENERGY SYSTEM YouTube

1 3 Aerobic & Anaerobic Energy YouTube

PPT Energy systems PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5880072

Aerobic system
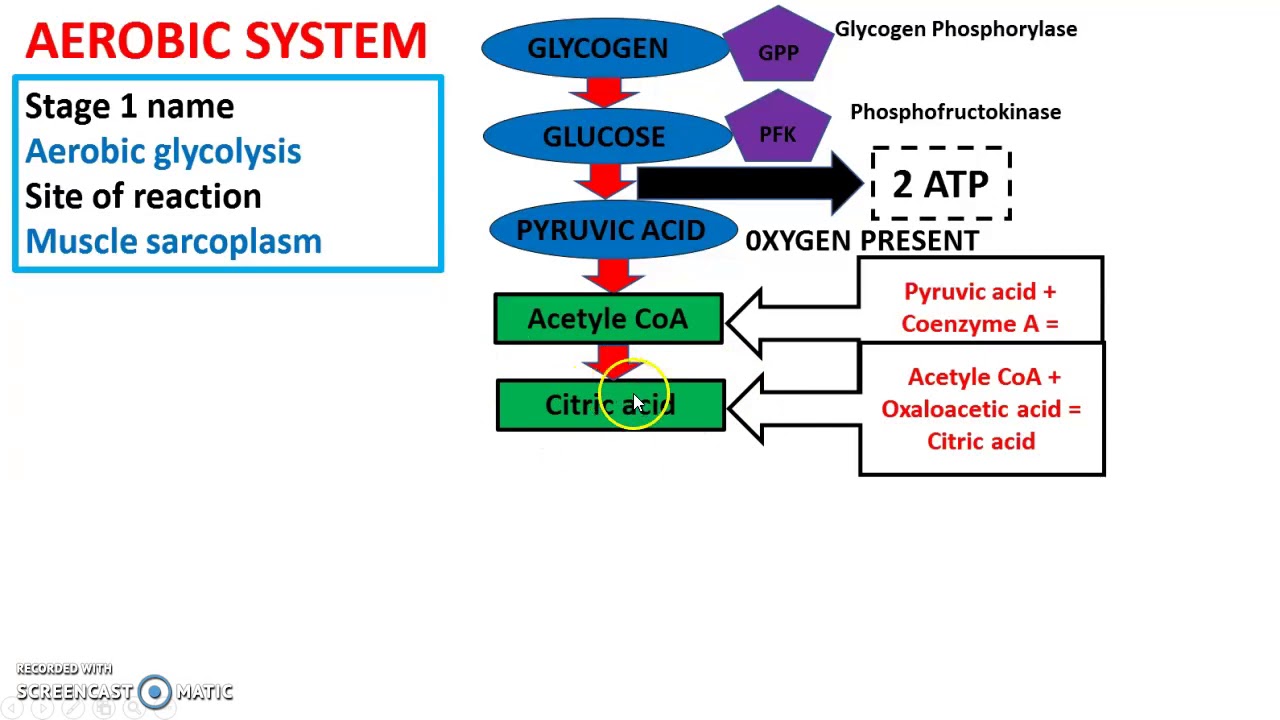
Aerobic energy system Pre lesson 2019 YouTube

Aerobic system

A Beginners Guide To The Aerobic Energy System & How We Test Power training, Beginners guide

Aerobic respiration and krebs cycle in Royalty Free Vector

PPT Aerobic and Anaerobic Pathways An Introduction to Energy Systems PowerPoint Presentation
Aerobic respiration is the process by which organisms use oxygen to turn fuel, such as fats and sugars, into chemical energy. In contrast, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine.. Oxidative energy production is the primary means of ATP production during rest and for activities that last for 2 minutes or longer. Although other forms of energy production assist in ATP production at any given time, long duration exercise sessions rely on this aerobic pathway. Also, in contrast to other forms of ATP production, the oxidative.